What is VLAN?
A VLAN (virtual local area network) is a logical group of workstations, servers and network devices that appear to be on the same LAN despite their geographical distribution. A VLAN allows a network of computers and users to communicate in a simulated environment as if they exist in a single LAN and are sharing a single broadcast and multicast domain. VLANs are implemented to achieve scalability, security and ease of network management and can quickly adapt to change in network requirements and relocation of workstations and server nodes.
What is VLAN Tagging?
VLAN Tagging in ESX (VST,EST & VGT)
Let’s cover from the basics. I hope you will be aware about the basics of VMware Virtual Network and architecture of standard and distributed switch. It is also important to understand the difference between standard virtual switches and distributed virtual switches.
There are 3 types of tagging available in vSphere.
1.Virtual Switch Tagging (VST)
2.External Switch Tagging (EST)
3.Virtual Guest Tagging (VGT)
VLAN tagging is determined by the VLAN value specified at the port group and it tells the vSwitch or Phyiscal switch or Virtual machines to how to handle the VLAN tagging.
1. Virtual Switch Tagging (VST)
1.1 VST uses 802.1q VLAN trunks and tagged traffic.
1.2 Tagging for all packets is performed by the Virtual Switch before leaving the ESX/ESXI host
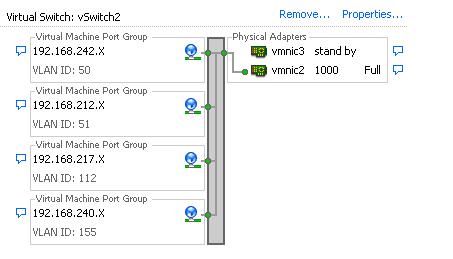
1.3 Port groups on the Virtual switch of ESX server should be configured with VLAN ID (1-4094)
1.4 vSwitch responsibilty is to strip off the vlan tag and send packet to virtual machine in corresponding port group.
1.5 Reduces the number of Physical nics on the server by running all the VLANs over one physical nic. Better solution would be keep 2 nics for redundancy.
1.6 Reduces number of cables from ESX server to physical switch.
1.7 The physical switch port connecting the uplink from the ESX should be configured as Trunk port.
1.8 virtual machine network Packet is delivered to vSwitch and before it is sent to physical switch the packet is tagged with vlan id according to the port group membership of originating virtual machine.
2.External Switch Tagging (EST)
2.1 In EST, ESX host doesn’t see any vlan tags and does not handle any VLAN tagging.
2.2 All the tagging operation is done by physical switch and virtual switch is not aware about that.
2.3 Number of physical nics = no of VLANs connected to ESX
2.4 Port groups on the Virtual switch of ESX server need not to be configured with the VLAN number or configure VLAN ID 0 (if it is not native VLAN)
2.5 Count of NICS and cable connected to ESX is more as compared to VST approach.
2.6 The physical switch port connecting the uplink from the ESX should be configured as Access port assigned to specific Virtual LAN
2.7 virtual machine network Packet is delivered to physical switch without any tagging operation performed by the virtual switch.
3. Virtual Guest Tagging (VGT)
3.1 you must install 8021.Q VLAN trunking driver instide virtual machine guest opearting system.
3.2 All the tagging is performed by the virtual machine with use of trunking driver in the guest.
3.3 Virtual LAN tags are understandable only between the virtual machine and external switch when frames are passed to/from virtual switches.
3.4 Virtual Switch will not be involved or aware of this operation. Vswitch only forwards the packets from Virtual machine to physical switch and will not perform any operation.
3.5 Port group of the virtual machine should be configured with ID 4095
3.6 The physical switch port connecting the uplink from the ESX should be configured as Trunk port
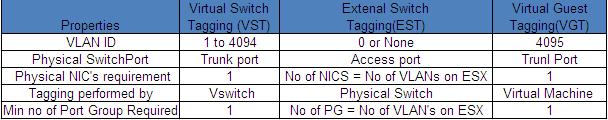
Below is comparison table for the people want a comparison under single table
I hope this post is informative for you. Thanks for reading. Be social and share it in social media like Google+, Facebook and twitter , if you feel worth sharing it.